Aside on Memory
Latches
Flip-Flops
Clocks
Abstract FSM memory

For physical logic gates, we have a timing issue :
The input
&
current state
must be in the same "time frame"
could represent 0100.
It could also represent others, such as 011000.
It all depends on the clock.
Typically we want the signal to be stable when the clock ticks.
A sequential logic circuit is designed with a specific clock rate in
mind.
At a different clock rate
Flip-Flops remember the signal value when the clock ticks
By this kind of alignment flip-flops hold the state value between clocks so that
combinational logic has time to
react.
The clock/flip-flop combo solves all kinds of timing problems, such
as ones of differing delay times in the combinational logic:

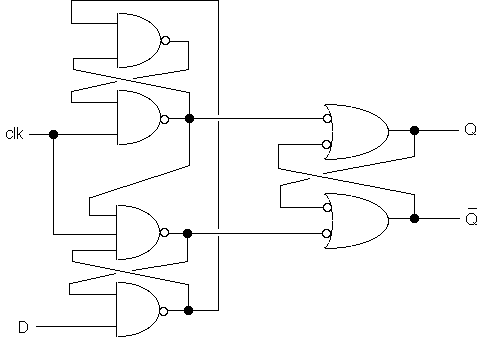
Construction of Flip-Flops
All physical gates have some switching delay
Generally, smaller delay is better.
Flip-Flops Exploit Delay to achieve memory.
A latch is a primitive form of flip-flop. It "tracks" its inputs, even without a clock.

Latch using Real
Gates (i.e. with delay)
"1/2" latch:

Redrawn
Summary